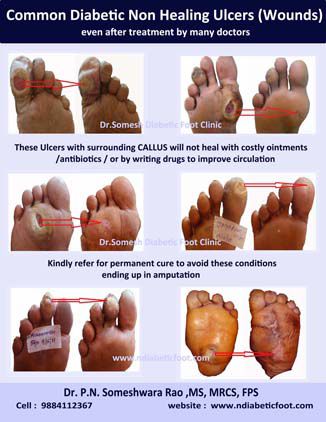
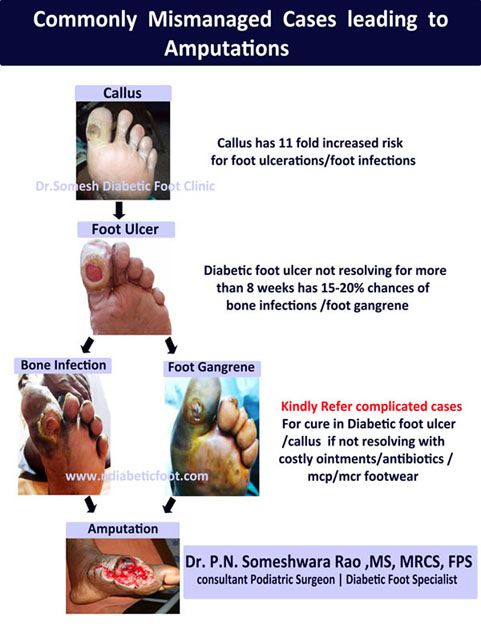
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. Foot Infections with osteomyelitis is usually preceded by non-healing c foot ulcers commonly seen in diabetic persons with neuropathy.
Clinically presents with
Fever
Swelling, warmth, redness and discolouration over the area of the infection
Pain in the area of the infection,
Sometimes we may not notice any of these initially
Causes
Common organism causing osteomyelitis are staphylococcus bacteria gram positive bacteria commonly seen in throat and skin infections.
Bacteria can damage bones through, including:
The bloodstream
Deep Injuries nearby bone
Bone Surgeries
Risk factors
Recent injury or orthopaedic surgery
Circulation disorders – wound not healing going deep up to bone
include: Poorly controlled diabetes, Peripheral artery disease, often related to smoking.
Problems requiring intravenous lines or catheters- acts a portal for bacteria to spread inside body which later infects bone –Examples of when this type of tubing might be used include:
Dialysis machine tubing
Urinary catheters
Prolonged intravenous tubing like central lines
Immune system dysfunction- include-Cancer treatment, uncontrolled diabetes, needing to take steroids
Illicit drugs
Complications
Bone death or necrosis – An infection damaging blood circulation within bone can lead to bone death.
Septic arthritis- infection spreading into a nearby joint.
Impaired growth
Skin cancer. Bone infection with foot risk of developing squamous cell cancer.
Prevention
Heal ulcers fast and check if signs of infection if delayed healing.
Diagnosis
Affected area might show tenderness, swelling or warmth. If you have a foot ulcer, foot doctor can check probe to bone test clinically suggesting osteomyelitis.
Lab Tests may include:
Blood tests
Raised white blood cells.
Imaging tests
X-rays. X-rays can show damage to your bone but not visible during initial few weeks.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – can detect recent osteomyelitis
Bone culture and sensitivity
Treatment
Sequestrectomy followed by intravenous antibiotics.
Amputation of the limb as a last resort,
Medications
Antibiotics according to culture should be given for 2 weeks if amputated or should be given for 8 -12 weeks if no amputation done.