Diabetic Neuropathy | Diabetic Foot Neuropathy
Diabetic foot infections are related directly to diabetic ulceration, which links directly to Diabetic Neuropathy. It has been well accepted that the lifetime incidence of diabetic foot ulcer is approximately 15% to 25%,Most of these problems are preventable through proper diabetic foot care and regular visits to your podiatrist at foot clinic.
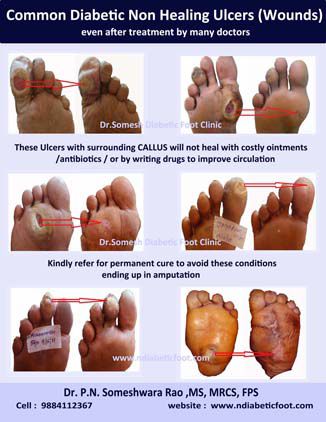
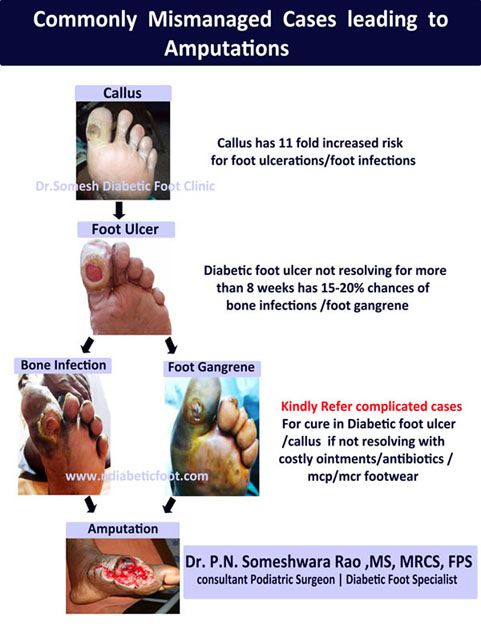
Nonhealing ulcers precede 85% of diabetic amputations, with the majority of these ulcerations stemming from Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy .
Longer and greater impaired glucose control results in more severe and irreversible neuronal changes.
Clinicians need to differentiate other causes of pain masquerading as Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy, such as plantar fasciitis,fracture, and ischemia. Other potential etiologies (nonhyperglycemic) for Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy include alcohol abuse, toxins, heavy metal poisoning, vitamin B12 deficiency, and monoclonal gammopathy
Your ability to detect sensations or vibration may be diminished. Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy allows injuries to remain unnoticed and untreated for lengthy periods of time. It may cause burning or sharp pains in feet and interfere with your sleep. Ironically, painful Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy may occur in combination with a loss of sensation. Neuropathy can also affect the nerves that supply the muscles in your feet and legs.
This ‘motor Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy‘ can cause muscle weakness or loss of tone in the thighs, legs, and feet, and the development of hammertoes, bunions, and other foot deformities.
Autonomic Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy–
Dysregulation of skeletal blood flow is thought to be a major factor in thedevelopment of Charcot arthropathy and neuropathic fracture dislocations.
Charcot arthropathy is a noninfectious destruction of bones and joints in patients with peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy, occurring in 0.5% to 2.5% of patients with diabetes. A current working theory for Charcot arthropathy starts with loss of sensation and position sense within lower extremity articulations.
The lack of proprioception and sensation results in an abnormally elevated reactive force through the joints. Subsequently, fracture and bone washout ensues, resulting in subchondral collapse and loss of normal bone architecture.
Ulceration and infection may occur when an insensate patient begins to bear weight on a deformed or mechanically unstable limb.
A second manifestation of autonomic Diabetic Neuropathy|Diabetic Foot Neuropathy is decreased production of protective essential fatty acids produces a dry, scaly skin that is prone to fissure and bacterial colonization. Surgeons caring for diabetics must recognize this condition and initiate treatment before embarking on surgery. Treatment includes skin conditioning with emollients,edema control, and efforts to decrease bacterial colonization (washing with chlorhexidine before surgery).